GSI: A Security Guarantee for Global Development
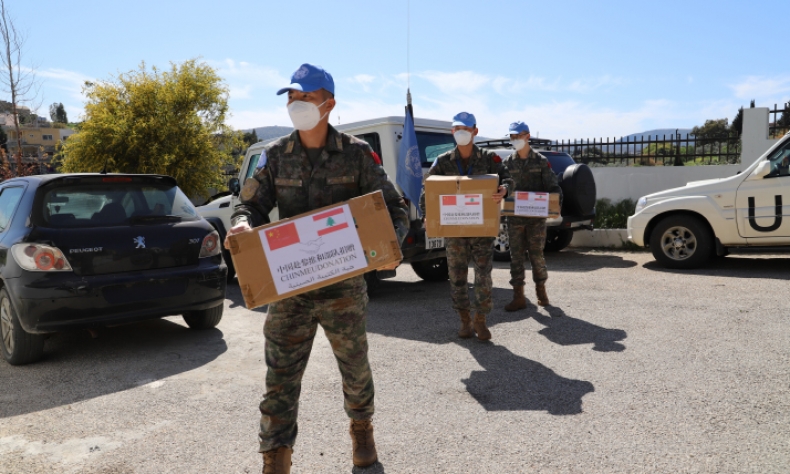

Global threats and challenges require global responses. Countries should strengthen strategic communication, enhance mutual trust, and jointly resolve conflicts, manage differences and eliminate the root causes of crises.
In a turbulent and changing world, global security governance faces severe challenges. World peace and development have come under threat, and confrontation and division in the field of human rights are intensifying. Many in the world politicize human rights, hindering the sustainable and healthy development of the international cause in this regard.
The international community must now build consensus and advance cooperation under frameworks such as the Global Security Initiative (GSI) proposed by China, which aims to improve the international diplomatic and security architecture as well as safeguard human rights through security, development and cooperation.
Common security
Human rights are first and foremost the right to life and survival, as well as the premise of production and life plus social development.
Citizen security centers on the development of the citizen to ensure the survival, reproduction and independence of individuals. Other human rights, such as the right to health and reputation, as well as the political, economic, social and cultural rights of citizens, are inseparable from the effective protection of such security.
Today’s world sees many risks of instability and insecurity in human rights. National security in turn guarantees the people’s security, making national sovereignty free from external interference a prerequisite for safeguarding human rights in all countries. The effective realization of citizen security depends on a peaceful and stable international environment; on countries respecting each other’s sovereignty and territorial integrity, and the social systems and governance approaches independently chosen; on the international community jointly following the path of peaceful development, and better protecting and promoting human rights.
The GSI came into being amid a complex and severe international environment and unprecedented global risks and challenges. Chinese President Xi Jinping first proposed the initiative at the opening ceremony of the Boao Forum for Asia Annual Conference 2022. Then, on February 21 this year, the Chinese Government issued the Global Security Initiative Concept Paper, which further elaborates on the initiative’s core concepts and principles, and identifies 20 priorities as well as five platforms and mechanisms of cooperation.
The GSI and its concept paper together represent China’s vision of common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable security in the new era. It is also China’s solution to maintaining world peace and stability, and promoting global human rights governance.
The idea of people’s security and the vision of a community with a shared future for humanity embodied in the GSI and its concept paper, as well as a series of corresponding concrete measures and proposals, echoed the Vienna Declaration and Program of Action adopted by the World Conference on Human Rights in 1993, reflecting the common values pursued by all of humanity.
As a responsible major country, over the years, China has been actively implementing the declaration and its related endeavors, and has made great efforts to develop its own human rights cause. The country has been seeking and promoting dialogue and cooperation with other countries and international organizations to jointly advance global governance on human rights.
Common development
The 1986 United Nations Declaration on the Right to Development defines the “right to development” as a new type of human right.
Security is the prerequisite and guarantee for development, and failure to develop is the greatest insecurity. At present, global development remains unbalanced, uncoordinated and inadequate, negatively impacting the full enjoyment of human rights by people around the world, especially in developing countries.
How to build consensus, seek security for the world’s economic recovery and development, promote global human rights governance, and achieve common security has become a topic of common concern.
In this regard, the GSI, which champions mutual respect, the indivisibility of security and the building of a security community with a shared future, is exploring a new security approach featuring dialogue rather than confrontation, partnership rather than alliance, and win-win rather than zero-sum.
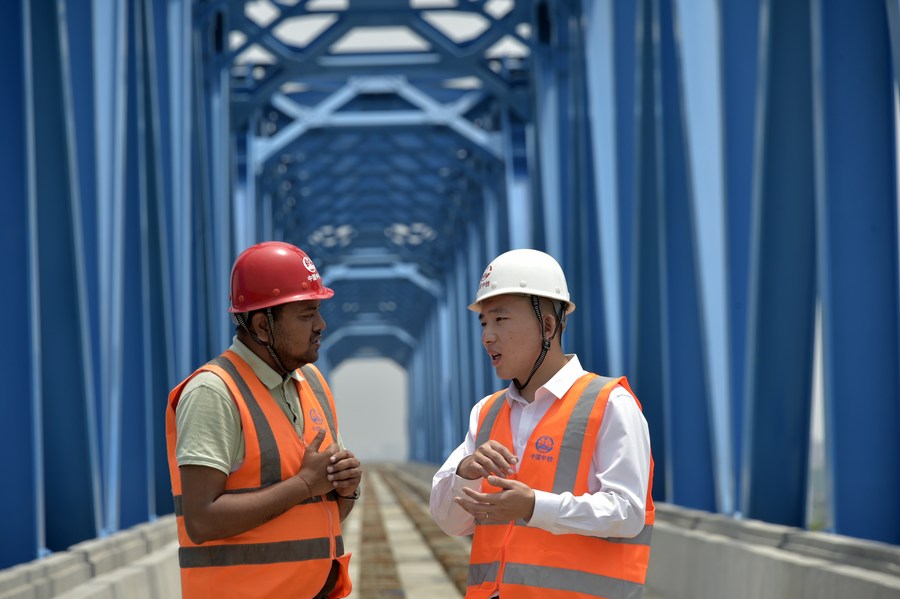

In 2013, China proposed the Belt and Road Initiative to boost connectivity along and beyond the ancient Silk Road routes. By June, 152 countries and 32 international organizations had signed more than 200 documents on Belt and Road cooperation with China.
Practices have proved that the only way to achieve sustainable security, address global crises and maintain long-term development is to respect and safeguard the security of every country and maintain security in both traditional and non-traditional fields, promote interconnectivity among countries, adhere to openness and inclusiveness, resolve conflicts through development and eliminate the breeding ground for insecurity.
An alternative
With the advancement of globalization after the end of the Cold War, peace and security, development and human rights together constituted, and constitute, the main contents of international exchanges and cooperation.
Cross-border security issues and domestic security challenges that have international implications, be they armed conflicts, international organized crime, deadly infectious diseases or environmental degradation, all require extensive international cooperation to manage.
However, global society still faces a growing deficit of governance, trust, development and peace, and to achieve universal security and promote common development remains an arduous task. In today’s world, there is no paradise of absolute security and security issues are more interconnected, transnational and diverse. Countries should put aside their differences, search for consensus and work together in dealing with the issue of international insecurity.

War and sanctions are never the means to resolve disputes. Security issues often stretch beyond national borders and the vulnerabilities of a country may lead to its exposure to more external risks, rendering it even more vulnerable. When the security problems of a country accumulate to a certain level, they can spill over into regional and even global issues.
The GSI could be a solution adopted by countries to pursue common, comprehensive, cooperative and sustainable global security, and transform the global governance system into one featuring extensive consultation, joint contribution and shared benefits.
Global threats and challenges require global responses. Countries should strengthen strategic communication, enhance mutual trust, and jointly resolve conflicts, manage differences and eliminate the root causes of crises.
No matter how the world situation changes, China will always be a builder of world peace, a contributor to global development and a defender of the international order with the UN Charter at its core. It will advocate and promote the GSI’s implementation, providing a security guarantee for carrying forward initiatives such as the Global Development Initiative, aiming to steer global development toward a new stage of balanced, coordinated and inclusive growth, the Global Civilizations Initiative, outlining the way to transcend estrangement, clashes and superiority between different cultures and societies, and the Belt and Road Initiative.
China is determined to achieve national rejuvenation through a Chinese path to modernization. In the process, it will deepen mutually beneficial cooperation with other countries and promote the building of a community with a shared future for humanity—with universal security.
The author is executive director of the Research Center of Science and Technology and Human Rights, Beijing Institute of Technology.
 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 Linkedin
Linkedin
 Google +
Google +










