BeiDou’s Completion Will Wind Up the Monopoly Era of GPS

Chinese technology has come of age, and while breaking the monopoly of traditional entities, it is making an invaluable contribution to the global scientific progress.
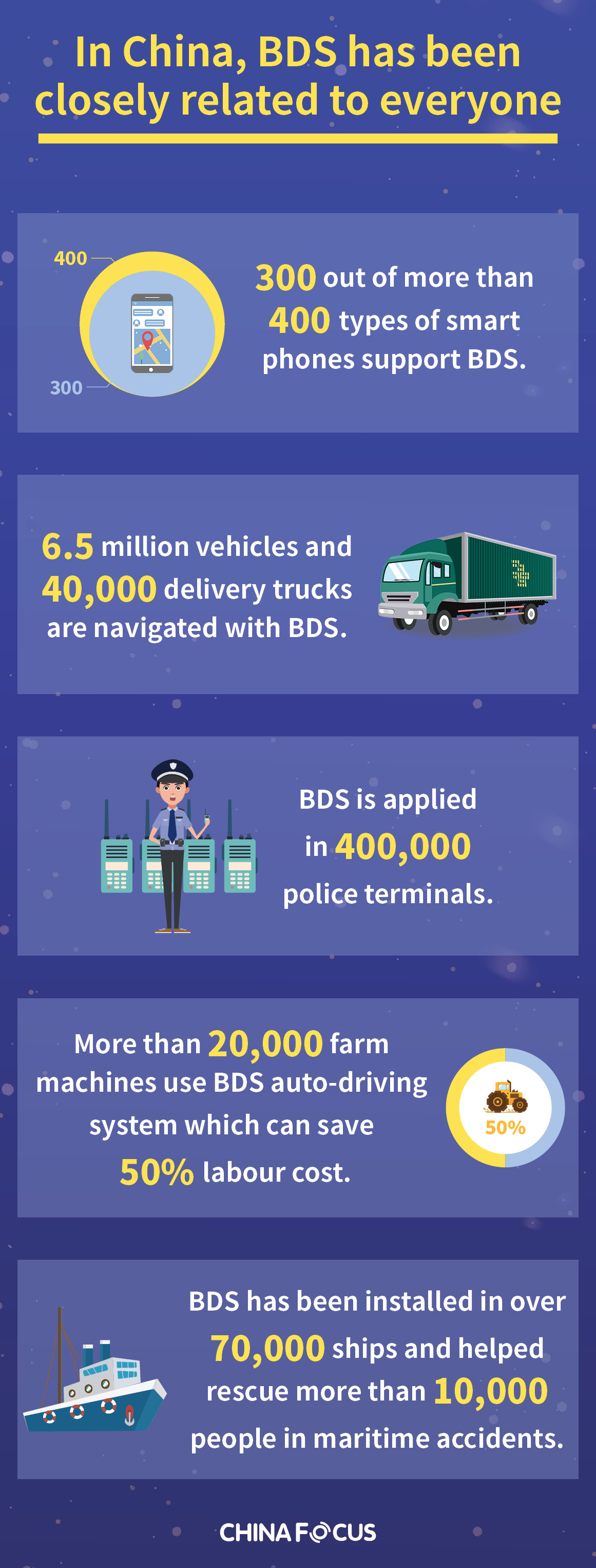
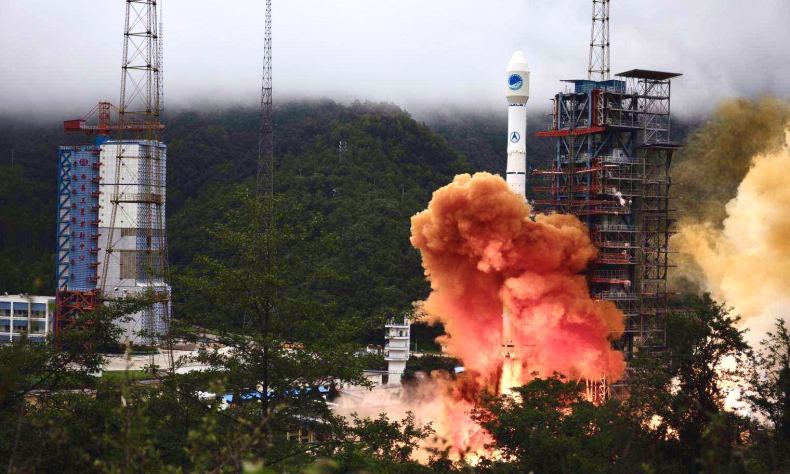
With the launch of the final satellite in the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) on June 23, China has completed the installation of the third generation of the network. This marks one of the most significant milestones in China’s technological journey in space utilization.
The independent development and operation of the system took 20 years, over 100,000 experts and more than 300 domestic institutes and enterprises to mature and set out on the path of becoming the most advanced navigational facility ever. While providing all-weather and accurate positioning services, BDS has already come to surpass many capabilities of the US-launched Global Positioning System (GPS) – a much older technological feat.
BDS’s biggest strength is its accuracy
A scrutinous look at the superiority of BDS reveals that accuracy is its biggest strength. With decimeter-level dynamic positioning and centimeter-level static positioning, it can provide location services down to the accuracy of 10 cm in the Asia-Pacific region.
The GPS, meanwhile, has the limitation of rendering a maximum of 30 cm of accuracy. This is because BeiDou uses much higher bandwidth under the concept of Precise Point Positioning function provided by its three Geostationary Earth Orbit satellites.
The higher accuracy of BDS has introduced new concepts in global positioning usage. Precision at the sub-meter level allows the technology’s application in wearable devices like children’s watches and bracelets for the elderly. As its product ecosystem will continue to sprout, it will be possible to mass manufacture inexpensive and small-sized tracking devices. Losing sight of anything or anyone loved will then be a thing of the past.
BDS will be on e-commerce
A greater impact would be on e-commerce. The cheaper and smaller BeiDou tracking devices will be embedded in packages, allowing sellers and buyers to actively follow their delivery status and make further commitments to clients with confidence.
China’s existing leadership in e-commerce will, therefore, strengthen, while simultaneously assisting other stakeholders in improving their revenues.
The function of the text messaging that the GPS does not have
Then there is BeiDou’s advantage of the text messaging that the GPS does not have. Presently, we are dependent on cell phones to request for help in cases of emergency. Due to the drawback of limited coverage in remote areas, people shift to the relatively expensive satellite phones.
But with the messaging feature of BeiDou, a new concept of connected mobility is emerging.
Thousands of fishing boats in China have already installed BDS, which enables them to communicate in times of distress. The same is true for outdoor sportspeople who are often outside of cell phone coverage in mountains and remain vulnerable to disaster situations. As 5G is changing the way we connect in urban areas, text messaging through BeiDou is likewise changing the way people connect in the remotest of areas.
The win-win aspiration of BDS
BDS, being a Chinese system, has another inherent Chinese characteristic: the win-win aspiration. Under this endeavor, China is promoting compatibility with other navigation systems. Traditionally, western technologies have attempted to maintain their monopoly for commercial and other reasons. BDS instead aims to become a global good so that all people around the world can benefit.
For this purpose, China has established a coordination mechanism with the US which ensures signal interoperability. In addition to that, China and the EU are cooperating in frequency coordination. But the most extensive collaboration that BDS has is with Russia’s GLONASS, abbreviated from Global Navigation Satellite System.
BDS and GLONASS have been cooperating since 2018 when an agreement was signed between the two sides to promote navigational equipment making use of both the systems. With monitoring stations installed in the two countries, correcting navigation signals will improve performance and allow operators to seamlessly switch from one network to the other. Moreover, users will benefit from GLONASS’s coverage in high-altitude areas and BeiDou’s coverage in low-altitude areas.
Partnership between Russian and Chinese systems is all the more important in the face of the recent crackdown against Chinese technologies by the US. It was only a matter of time that China had to reduce its reliance on American technology and products and develop self-sufficiency in navigation as well as in all high-end requirements.
Today’s communication and transportation are increasingly becoming sophisticated. And as the world is equally becoming dependent on them to efficiently deliver products and services, reliance on GPS as the single source of navigational guidance was becoming riskier.
BDS provides the world an alternative
BDS has ultimately provided the world an alternative. With a single player or with the monopoly of a single player in the market, development and innovation almost becomes non-existent. The completion of BDS is now giving users an additional option for comparison. They can either opt for the better one or make use of the combination of both.
It is also a fact that US technologies have always been provided to customers with attached strings. Whenever they are exported, they come with preconditions on their usage and the continuity of maintenance support has remained dependent on the whims of US policies. China always adopts the approach of respecting national priorities of its foreign partners. In the case of BDS, too, its users can remain assured of support with no binding restrictions.
BDS will unleash a new era in global navigation and positioning
China is the rising power of the 21st century that does not hold any hegemonistic ambitions. However, due to his presumed insecurities, US President Donald Trump initiated a trade war with China in 2018. Though a phase one deal has significantly subdued its effects, it became a wake-up call for all countries to prepare for situations when the US attempts to undermine others’ economic success.
GPS is extensively used in commercial activities. If one day the US decides to regulate GPS signals to affect any other country’s economy, it will result in an unmanageable situation. A close similarity to this predicament was the U.S. government’s pressure on Google to discontinue Android supplies to Huawei.
Then there are reasons related to national security that have forced many governments to look for alternatives to GPS. Of course, there will always be countries not aligning politically with the US. BeiDou provides them with the option of breaking free from a single system. After the impending completion of BDS, China is in a better position to secure its navigational requirements and offer the same to its partners.
From a technical perspective, BDS has several advantages over GPS. As its satellites use fewer orbit planes, it is far easier to maintain. It has more satellites than GPS, GLONASS or the European Galileo system. And lastly, its performance in covered settings is also superior, thereby giving it higher accuracy indoors, underground and underwater.
All things considered, the completion of the BDS network will unleash a new era in global navigation and positioning. With its improved features, it has brought cutting edge, yet affordable facilities that will bolster economic activity and augment the efficiency of supply chains. Chinese technology has come of age, and while breaking the monopoly of traditional entities, it is making an invaluable contribution to the global scientific progress.
Copy Editors: Cai Hairuo, Wang Yuzhen
Graphic Designer: Gao Ming
 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 Linkedin
Linkedin
 Google +
Google +